Answer:
The final speed of puck 1 is 0.739 m/s towards west and puck 2 is 2.02 m/s towards east .
Step-by-step explanation:
Let us consider east as positive direction and west as negative direction .
Given
mass of puck 1 ,
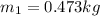
mass of puck 2 ,
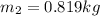
initial speed of puck 1 ,
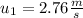
initial speed of puck 2 ,
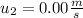
Final speed of puck 1 and puck 2 be
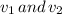 respectively
respectively
Apply conservation of linear momentum
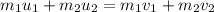
=>
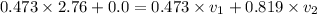
=>
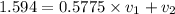 -----(A)
-----(A)
Since collision is perfectly elastic , coefficient restitution e=1
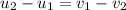
=>
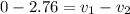 ------(B)
------(B)
From equation (A) and (B)
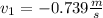
and
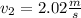
Thus the final speed of puck 1 is 0.739 m/s towards west and puck 2 is 2.02 m/s towards east .