Answer:
L = 46.35 m
Step-by-step explanation:
GIVEN DATA
\dot m = 0.25 kg/s
D = 40 mm
P_1 = 690 kPa
P_2 = 650 kPa
T_1 = 40° = 313 K
head loss equation
![[(P_1)/(\rho) +\alpha (v_1^2)/(2) +gz_1] -[(P_2)/(\rho) +\alpha (v_2^2)/(2) +gz_2] = h_l +h_m](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/engineering/college/q4p99til9jqgqn08nnjbzwpzg1kjf2t0qk.png)
where
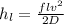
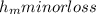
density is constant
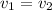
head is same so,
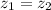
curvature is constant so
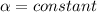
neglecting minor losses
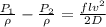
we know
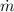 is given as
is given as
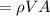
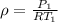
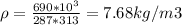
therefore
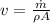
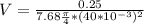
V = 25.90 m/s
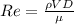
for T = 40 Degree,
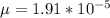
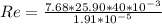
Re = 4.16*10^5 > 2300 therefore turbulent flow
for Re =4.16*10^5 , f = 0.0134
Therefore
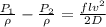
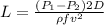
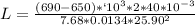
L = 46.35 m