For this case we must find the domain of the following function:
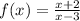
By definition, the domain of a function is given by all the values for which the function is defined. The given function is not defined when the denominator is equal to zero, that is:
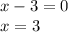
Thus, the domain of the function is given by all real numbers except 3.
Answer:
x other than 3