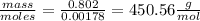Answer:
Molar mass of vitamin K = 450.56\frac{g}{mol}[/tex]
Step-by-step explanation:
The freezing point of camphor = 178.4 ⁰C
the Kf of camphor = 37.7°C/m
where : m = molality
the relation between freezing point depression and molality is
Depression in freezing point = Kf X molality
Where
Kf = cryoscopic constant of camphor
molality = moles of solute dissolved per kg of solvent.
putting values
2.69°C = 37.7°C/m X molality
molality = 0.0714 mol /kg
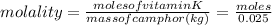
moles of vitamin K = 0.0714X0.025 = 0.00178 mol
we know that moles are related to mass and molar mass of a substance as:
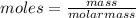
For vitamin K the mass is given = 0.802 grams
therefore molar mass =