Answer:
Implicit type casting means the type casting done by the compiler during compilation of program whereas Explicit type casting means the programmer explicitly type casts the variables. This is the difference implicit and explicit type casting.
Explanation:
Type casting means the conversion of one data type into another data type. There are two types of type casting. They are Implicit type casting and Explicit type casting.
Implicit type casting: The type casting which is done by the compiler during the compilation of a program. This occurs when we assigning smaller data type to larger data type and also both the data type are compatible. Below example clears the above concepts.
Ex:
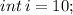
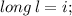
In the above example " i " is " int " data type whereas " l " is long data type but as we assigned the value of " i " to " l ". Here " int " and " long " are compatible data types and we assigned smaller data type ( int - i ) to larger data type ( long - l ) implicit type casting occurs.
Explicit type casting: The type casting which is done by the programmer explicitly to convert one data type into other data type. If we want to assign a value of larger data type to smaller data type explicit type casting is required. Below example clears the above concepts.
Ex:
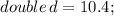
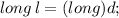
In the above example " d " is " double " data type whereas " l " is " long " data type. Here we are explicitly type casting to change larger data value ( double - d ) to smaller data value ( long - l ).