Answer:
The value of dissociation constant from this experimental data fro phenol is
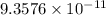 .
.
Step-by-step explanation:
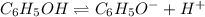
Initially c 0 0
At eq'm
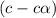
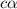
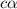
Concentration of phenol , initially = c = 0.529 M
Degree of dissociation =
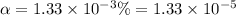
An expression for dissociation constant is given as:
![K_a=([C_6H_5O^-][H^+])/([C_6H_5OH])](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/k4qufl71439ivrgs9hl94zbppdgd821d1a.png)
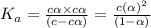
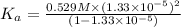
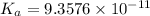
The value of dissociation constant from this experimental data fro phenol is
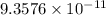 .
.