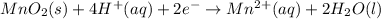Answer:
Step-by-step explanation:
Reduction is a process where electrons are gained and acidic solution means presence of
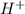 ions.
ions.
Reduction of
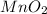 to
to
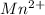
Mn is in +4 oxidation state in
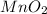 which goes to +2 state in
which goes to +2 state in
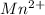 by gain of 2 electrons.
by gain of 2 electrons.
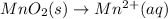
In order to balance oxygen atoms:
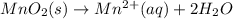
In order to balance hydrogen atoms:
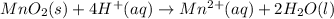
In order to balance charges:
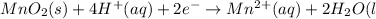
Thus the net balanced half reaction for the reduction of solid manganese dioxide to manganese ion in acidic aqueous solution is: