Answer: 0.7941
Step-by-step explanation:
Given : Suppose a study finds that the wing lengths of houseflies are normally distributed with mean :
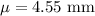
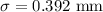
Let X be the random variable that represents the wing lengths of a randomly selected housefly.
Z-score :
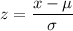
For x = 4 mm
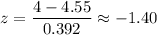
For x = 5 mm
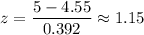
Now, the probability that a randomly selected housefly has a wing length between 4mm and 5mm is given by :-
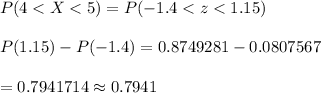
Hence, the probability that a randomly selected housefly has a wing length between 4mm and 5mm is 0.7941 .