The vector pointing from (2, 1) to (1, 3) points in the same direction as the vector
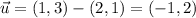 . The derivative of
. The derivative of
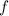 at (2, 1) in the direction of
at (2, 1) in the direction of
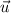 is
is
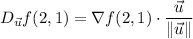
We have
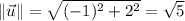
Then
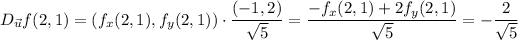
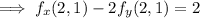
The vector pointing from (2, 1) to (5, 5) has the same direction as the vector
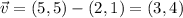 . The derivative of
. The derivative of
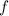 at (2, 1) in the direction of
at (2, 1) in the direction of
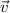 is
is
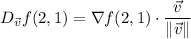
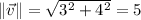
so that
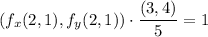
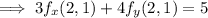
Solving the remaining system gives
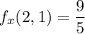 and
and
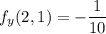 .
.