Answer:
The dissociation constant of phenol from given information is
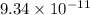 .
.
Step-by-step explanation:
The measured pH of the solution = 5.153
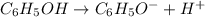
Initially c
At eq'm c-x x x
The expression of dissociation constant is given as:
![K_a=([C_6H_5O^-][H^+])/([C_6H_5OOH])](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/tdpdkaap28j4uhvcyzn59aksuz9cwsm9s4.png)
Concentration of phenoxide ions and hydrogen ions are equal to x.
![pH=-\log[x]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/ewxlzjvv4g40nxx89m9x3qz6unyhgmx8do.png)
![5.153=-\log[x]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/5si57ntz1ipckl7ohs67zvsxfx6ngow20n.png)
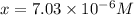
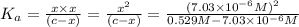
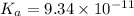
The dissociation constant of phenol from given information is
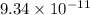 .
.