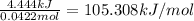Answer:
The heat of the reaction is 105.308 kJ/mol.
Step-by-step explanation:
Let the heat released during reaction be q.
Heat gained by water: Q
Mass of water ,m= 1kg = 1000 g
Heat capacity of water ,c= 4.184 J/g°C
Change in temperature = ΔT = 26.061°C - 25.000°C=1.061 °C
Q=mcΔT
Heat gained by bomb calorimeter =Q'
Heat capacity of bomb calorimeter ,C= 4.643 J/g°C
Change in temperature = ΔT'= ΔT= 26.061°C - 25.000°C=1.061 °C
Q'=CΔT'=CΔT
Total heat released during reaction is equal to total heat gained by water and bomb calorimeter.
q= -(Q+Q')
q = -mcΔT - CΔT=-ΔT(mc+C)
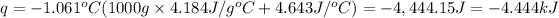
Moles of propane =
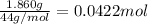
0.0422 moles of propane on reaction with oxygen releases 4.444 kJ of heat.
The heat of the reaction will be: