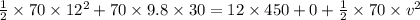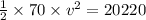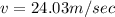Answer:
Speed at the bottom of the slope is 24.03 m /sec
Step-by-step explanation:
We have given speed of the cyclist v = 12 m/sec
She starts down a 450 m long that is 30 m high
Si distance = 450 m and height h = 30 m
Combined mass of cyclist and bicycle m = 70 kg
Drag force = 12 N
We have to find the speed at the bottom
According to conservation theory
KE +PE = work done by drag force + KE + PE
As we know that at the bottom there will be no potential energy
So