Answer : The value of
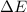 of the reaction is, 479.958 KJ/mole
of the reaction is, 479.958 KJ/mole
Explanation :
The relation between the internal energy and enthalpy of reaction is:

where,
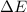 = internal energy of the reaction = ?
= internal energy of the reaction = ?
 = enthalpy of the reaction = 483.6 KJ/mole = 483600 J/mole
= enthalpy of the reaction = 483.6 KJ/mole = 483600 J/mole
From the balanced reaction we conclude that,
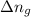 = change in the moles of the reaction = Moles of product - Moles of reactant = 3 - 2 = 1 mole
= change in the moles of the reaction = Moles of product - Moles of reactant = 3 - 2 = 1 mole
R = gas constant = 8.314 J/mole.K
T = temperature =
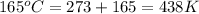
Now put all the given values in the above formula, we get:
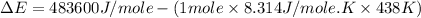
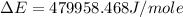
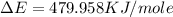
Therefore, the value of
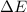 of the reaction is, 479.958 KJ/mole
of the reaction is, 479.958 KJ/mole