Answer: There are now 2.07 moles of gas in the flask.
Step-by-step explanation:
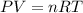
P= Pressure of the gas = 697 mmHg = 0.92 atm (760 mmHg= 1 atm)
V= Volume of gas = volume of container = ?
n = number of moles = 1.9
T = Temperature of the gas = 21°C=(21+273)K= 294 K (0°C = 273 K)
R= Value of gas constant = 0.0821 Latm\K mol
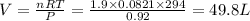
When more gas is added to the flask. The new pressure is 775 mm Hg and the temperature is now 26 °C, but the volume remains same.Thus again using ideal gas equation to find number of moles.
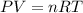
P= Pressure of the gas = 775 mmHg = 1.02 atm (760 mmHg= 1 atm)
V= Volume of gas = volume of container = 49.8 L
n = number of moles = ?
T = Temperature of the gas = 26°C=(26+273)K= 299 K (0°C = 273 K)
R= Value of gas constant = 0.0821 Latm\K mol
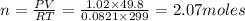
Thus the now the container contains 2.07 moles.