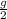Answer:
Step-by-step explanation:
Given
mass of stone
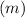 =0.250 kg
=0.250 kg
Let initial velocity with which it is thrown upward is u
therefore after time t it's velocity is zero at highest point
t=
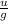
where g= gravity at earth
therefore
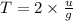 -------1
-------1
Now same thing is done in Planet X where gravity is g'
therefore time taken by stone to reach surface is
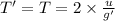 -------2
-------2
Divide 1 & 2
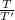 =
=
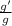
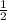 =
=
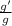
g'=