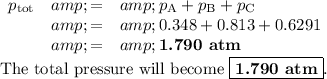Answer:
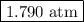
Step-by-step explanation:
To calculate the partial pressure of the third gas, we can use the Ideal Gas Law:
pV = nRT
Data:
V = 8.55 L
n = 0.210 mol
T = 39 °C
Calculations:
T = (39 + 273.15) K = 312.15 K

According to Dalton's Law of Partial Pressures, each gas exerts its own pressure independently of the others.