Answer:

Step-by-step explanation:
1. Miles travelled in an average month
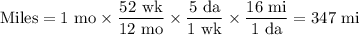
2. Using a gasoline powered vehicle
(a) Moles of heptane used
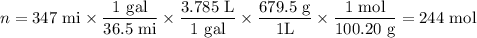
(b) Equation for combustion
C₇H₁₆ + O₂ ⟶ 7CO₂ + 8H₂O
(c) Moles of CO₂ formed
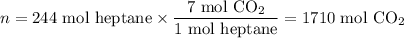
(d) Volume of CO₂ formed
At 20 °C and 1 atm, the molar volume of a gas is 24.0 L.
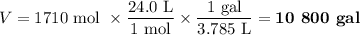
3. Using an electric vehicle
(a) Theoretical energy used
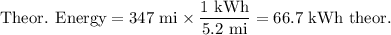
(b) Actual energy used
The power station is only 85 % efficient.
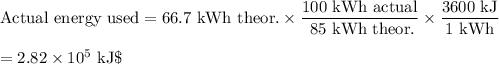
(c) Combustion of CH₄
CH₄ + 2O₂ ⟶ CO₂ +2 H₂O
(d) Equivalent volume of CO₂
The heat of combustion of methane is -802.3 kJ·mol⁻¹
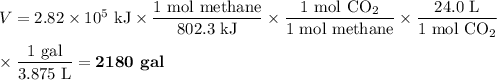
4. Comparison
