Answer:
a) W = 2.26 × 10⁻²¹ J
b) V = - 0.00706 Volts
Step-by-step explanation:
Given:
The surface charge density, σ = +5.21 pC/m²
Charge of the particle, q₀ = 3.20 × 10⁻¹⁹
distance, d = 2.44 cm = 0.024 m
Now, the electric field (E) due to the uniformly charged sheet is given as:
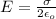
a) The work done is given as:
W = q₀Ed
substituting the values, we get
W =
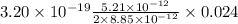
W = 2.26 × 10⁻²¹ J
b) The electric potential (V) at point P is given as:
V = - Ed
substituting the values, we get
V = - (
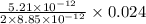 )
)
V = - 0.00706 Volts