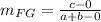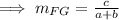Answer:
See explanation
Explanation:
a) To prove that DEFG is a rhombus, it is sufficient to prove that:
- All the sides of the rhombus are congruent:
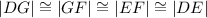
- The diagonals are perpendicular
Using the distance formula;
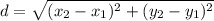
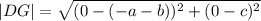
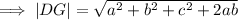
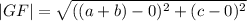
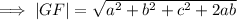
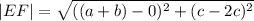
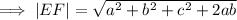
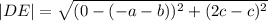
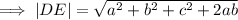
Using the slope formula;
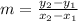
The slope of EG is
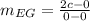
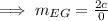
The slope of EG is undefined hence it is a vertical line.
The slope of DF is
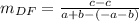
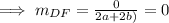
The slope of DF is zero, hence it is a horizontal line.
A horizontal line meets a vertical line at 90 degrees.
Conclusion:
Since
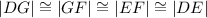 and
and
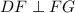 , DEFG is a rhombus
, DEFG is a rhombus
b) Using the slope formula:
The slope of DE is
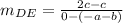
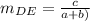
The slope of FG is