Answer:
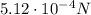
Step-by-step explanation:
The force exerted between two current-carrying wires is given by
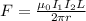
where
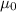 is the vacuum permeability
is the vacuum permeability
I1 and I2 are the two currents
L is the length of the segment of wire on which we want to calculate the force
r is the distance between the wires
In this problem we have:
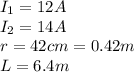
Substituting into the formula, we find:
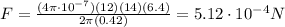
And since the direction of the two currents is opposite, the force between the wires is repulsive.