Answer:
437.49 K
Step-by-step explanation:
Given:
The number of moles, n = 20.5 moles
Initial pressure P₁ = 2.86 × 10⁵ Pa
Initial temprature, T₁ = 300 K
Cp = 20.79 J/K/mole
Now
the Initial volume V₁ is given as
V₁ =
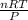
where, R is the gas constant
substituting the value in the above equation, we get
V₁ =
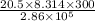
or
V₁ =0.178 m³
the energy added (Q) =58600 J
also, we know that
Q = nCp(T ' - T )
where, T₂ is the final temperature
substituting the values in the equation, we get
58600 = 20.5 × 20.79 × (T ' - 300 )
T₂ - 300 = 137.49
or
T₂ = 437.49 K