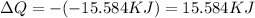Answer:
a) Work done by gas = -15.584 KJ
b) Energy transferred = 15.584 KJ
Step-by-step explanation:
Given:
Initial volume of the gas, V₁ = 5.39 m³
Final volume, V₂ = 2.84 m³
Temperature, T = 27.2°C = 273+27.2 = 300.2K
Number of moles, n = 9.75 mol
a) Work done for the given isothermal process is
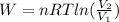
where, R is the ideal gas constant = 8.31 J/mol.K
substituting the values we get,
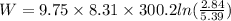
or
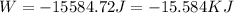
b) From the first law of thermodynamics
change in internal energy = Heat added - Work done
or,
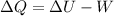
Now for the isothermal process, ΔU = 0
thus,
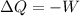
or