Answer:
a)
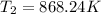 ,
,
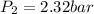
b)
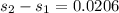 KW/K
KW/K
Step-by-step explanation:
P=4200 KW ,mass flow rate=20 kg/s.
Inlet of turbine
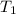 =807°C,
=807°C,
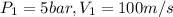
Exits of turbine
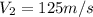
Inlet of diffuser
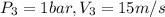
Given that ,use air as ideal gas
R=0.287 KJ/kg-k,
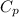 =1.005 KJ/kg-k
=1.005 KJ/kg-k
Now from first law of thermodynamics for open system at steady state
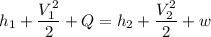
Here given that turbine is adiabatic so Q=0
Air treat ideal gas PV=mRT, Δh=
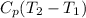
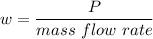
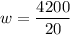
w=210 KJ/kg
Now putting the values
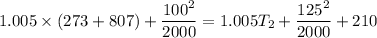
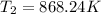
Now to find pressure
We know that for adiabatic
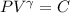 and for ideal gas Pv=mRT
and for ideal gas Pv=mRT
⇒
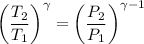
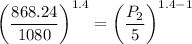
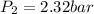
For entropy generation
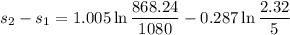
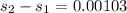 KJ/kg_k
KJ/kg_k
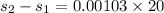 KW/K
KW/K
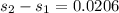 KW/K
KW/K