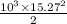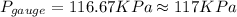Answer:(b) 117 KPa
Step-by-step explanation:
Given
Voulme
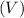 =3 L
=3 L
diameter of nozzle
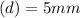
time
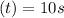
Flow rate
![\left ( \dot{Q}\right )=3* 10^{-4] m^3/s](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/engineering/college/56rb36emhyqz62jb5o5modp8d6wf88o0xm.png)
Exit velocity at nozzle
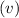 =
=
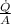
v=
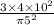 =15.27m/s
=15.27m/s
Applying bernoulli's equation
1 is top point and 2 is bottom point
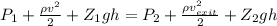
neglecting height variation as it is very small
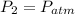
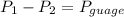
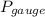 =
=