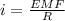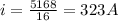Answer:
i = 323 A
Step-by-step explanation:
Initial flux due to magnetic field from the coil is given as
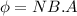
here we will have
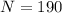
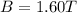
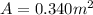
now the flux is given as
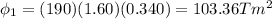
finally current in the electromagnet changed to zero
so final flux in the coil is zero
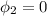
now we know that rate of change in flux will induce EMF in the coil
so we will have
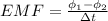
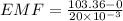
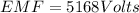
now induced current is given as