Step-by-step explanation:
According to Avogadro's law, equal volumes of all the gases at same temperature and pressure will also, have same number of molecules.
That is,
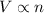
or
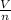 = k
= k
Since, it is given that
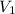 is 6.13 L,
is 6.13 L,
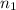 is 8.51 mol, and
is 8.51 mol, and
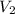 is 18.5 L.
is 18.5 L.
Hence, calculate the
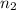 as follows.
as follows.
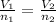
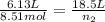
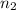 = 0.35 mol
= 0.35 mol
Thus, we can conclude that the number of moles of gas added to the container is 0.35 mol.