Answer:
the work done during this cooling is −28.7 kJ
Step-by-step explanation:
Given data
mass (m) = 1 kg
r = 287 J/kg-K
pressure ( p) = 50 kPa
temperature (T) = 100°C = ( 100 +273 ) = 373 K
to find out
the work done during this cooling
Solution
we know the first law of thermodynamics
pv = mRT ....................1
here put value of p, m R and T and get volume v(a) when it initial stage in equation 1
50 v(a) = 1 × 0.287 × 373
v(a) = 107.051 / 50
v(a) = 2.1410 m³ .......................2
now we find out volume when temperature is 0°C
so put put value of p, m R and T and get volume v(b) when temperature is cooled in equation 1
50 v(b) = 1 × 0.287 × 273
v(a) = 78.351 / 50
v(a) = 1.5670 m³ .......................3
by equation 2 and 3 we find out work done to integrate the p with respect to v i.e.
work done =
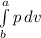
integrate it and we get
work done = p ( v(b) - v(a) ) ................4
put the value p and v(a) and v(b) in equation 4 and we get
work done = p ( v(b) - v(a) )
work done = 50 ( 1.5670 - 2.1410 )
work done = 50 ( 1.5670 - 2.1410 )
work done = 50 (−0.574)
work done = −28.7 kJ
here we can see work done is negative so its mean work done opposite in direction of inside air
'