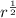Answer:
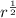
Step-by-step explanation:
Angular momentum, L = m v r
areal velocity =
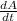
according to kepler's 2nd law
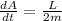
since, we know that
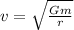
areal velocity=
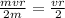
now substituting value of v in areal velocity we get
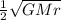
hence from above equation of rate of change of area swept i.e. areal velocity is proportional to