Answer: The freezing point of solution is -3.34°C
Step-by-step explanation:
Vant hoff factor for ionic solute is the number of ions that are present in a solution. The equation for the ionization of calcium nitrate follows:
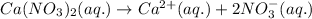
The total number of ions present in the solution are 3.
- To calculate the molality of solution, we use the equation:
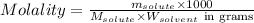
Where,
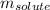 = Given mass of solute
= Given mass of solute
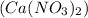 = 11.3 g
= 11.3 g
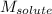 = Molar mass of solute
= Molar mass of solute
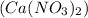 = 164 g/mol
= 164 g/mol
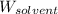 = Mass of solvent (water) = 115 g
= Mass of solvent (water) = 115 g
Putting values in above equation, we get:
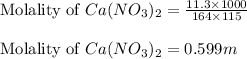
- To calculate the depression in freezing point, we use the equation:
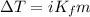
where,
i = Vant hoff factor = 3
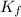 = molal freezing point depression constant = 1.86°C/m.g
= molal freezing point depression constant = 1.86°C/m.g
m = molality of solution = 0.599 m
Putting values in above equation, we get:
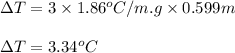
Depression in freezing point is defined as the difference in the freezing point of water and freezing point of solution.
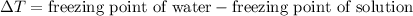
 = 3.34 °C
= 3.34 °C
Freezing point of water = 0°C
Freezing point of solution = ?
Putting values in above equation, we get:

Hence, the freezing point of solution is -3.34°C