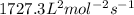Answer: Rate law=
![Rate=k[NO]^2[O_2]^1](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/3yj1d4ed09nym7igcph9i1xlulzgpnwduu.png)
Rate law constant is
Step-by-step explanation:
Rate law says that rate of a reaction is directly proportional to the concentration of the reactants each raised to a stoichiometric coefficient determined experimentally called as order.
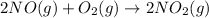
![Rate=k[NO]^x[O_2]^y](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/vg99yvximtx6hqrg5qmq8khbd55i3qx01r.png)
k= rate constant
x = order with respect to NO
y = order with respect to

n = x+y = Total order
a) From trial 1:
![8.55 x 10^(-3)=k[0.030]^x[0.0055]^y](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/t88uznwin6ma7fm0lxhzg6wqic4ydijjkr.png) (1)
(1)
From trial 2:
![1.71 x 10^(-2)=k[0.030]^x[0.0110]^y](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/6y8yq2toi51axtbqjl4tj2fkqaoyi4itnq.png) (2)
(2)
Dividing 2 by 1 :
![(1.71* 10^(-2))/(8.55* 10^(-3))=(k[0.030]^x[0.0110]^y)/(k[0.030]^x[0.0055]^y)](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/4oh7t62x355vsfj9b6vunpbhn8utargw0v.png)
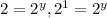 therefore y=1.
therefore y=1.
b) From trial 1 :
![8.55 x 10^(-3)=k[0.030]^x[0.0055]^y](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/t88uznwin6ma7fm0lxhzg6wqic4ydijjkr.png) (3)
(3)
From trial 3:
![3.42* 10^(-2)=k[0.060]^x[0.0055]^y](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/2lnzb858q1ts1zincllvweqqzjv5mf8u23.png) (4)
(4)
Dividing 4 by 3:
![(3.42* 10^(-2))/(8.55* 10^(-3))=(k[0.060]^x[0.0055]^y)/(k[0.030]^x[0.0055]^y)](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/8fchcsw8s3p19sjvxokee1yxunjs7ig91e.png)
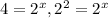 , x=2Thus rate law is
, x=2Thus rate law is
![Rate=k[NO]^2[O_2]^1](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/3yj1d4ed09nym7igcph9i1xlulzgpnwduu.png)
Thus order with respect to
 is 2 , order with respect to
is 2 , order with respect to
 is 1 and total order is 1+2=3.
is 1 and total order is 1+2=3.
Rate law is
![Rate=k[NO]^2[O_2]^1](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/3yj1d4ed09nym7igcph9i1xlulzgpnwduu.png)
b) For calculating k:
Using trial 1:
![8.55* 10^(-3)=k[0.030]^2[0.0055]^1](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/symnx5ne1wwniwlv6j7r9ep9m0gzl10vo3.png)
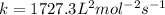
The value of rate constant is