Answer: 0.2 M
Step-by-step explanation:
Rate law says that rate of a reaction is directly proportional to the concentration of the reactants each raised to a stoichiometric coefficient determined experimentally called as order.
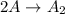
![rate=k[A]^2](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/physics/college/7ipco6dur0zsvk68rjme7y91nyukjewl9k.png)
Integrated rate law for second order kinetics is given by:
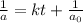
t= time taken for the reaction = 180 min
k = rate constant =
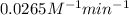
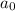 = initial concentration = 4 M
= initial concentration = 4 M
a= concentration left after time t = ?
Putting in the values we get:
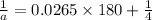
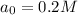
Thus the concentration of A after 180.0 min is 0.2M