Answer:
0.73kg
Step-by-step explanation:
let,
The mass of the water as
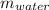
Given:
Mass of the aluminum,
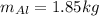
Initial temperature of the water,
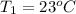
Initial temperature of the aluminum,
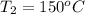
The final temperature of the aluminum,
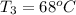
Now,
the heat gained by the water = the heat lost by the aluminium
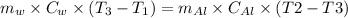
where,
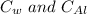 = specific heat of water and aluminium
= specific heat of water and aluminium
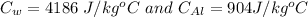
substituting the values in the equation, we get
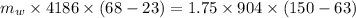
thus,
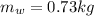
Hence, the required mass of the water required is 0.73kg