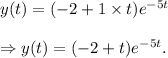Answer: The required solution is
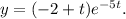
Step-by-step explanation: We are given to solve the following differential equation :
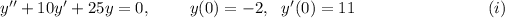
Let us consider that
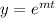 be an auxiliary solution of equation (i).
be an auxiliary solution of equation (i).
Then, we have
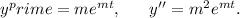
Substituting these values in equation (i), we get
![m^2e^(mt)+10me^(mt)+25e^(mt)=0\\\\\Rightarrow (m^2+10y+25)e^(mt)=0\\\\\Rightarrow m^2+10m+25=0~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~[\textup{since }e^(mt)\\eq0]\\\\\Rightarrow m^2+2* m*5+5^2=0\\\\\Rightarrow (m+5)^2=0\\\\\Rightarrow m=-5,-5.](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/mathematics/college/v7f1qm46x3df5l4xgn23brbmtr95uft3fp.png)
So, the general solution of the given equation is
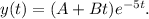
Differentiating with respect to t, we get
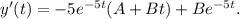
According to the given conditions, we have
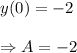
and
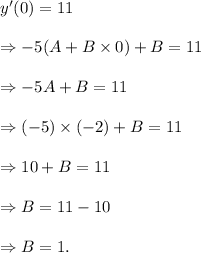
Thus, the required solution is