Answer:
At $2 supply and demand are in equilibrium for 32 quantity
Step-by-step explanation:
We have to solve for the linear equation first, and then calcualte the equilibrium price and quantity
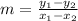
Demand
![\left[\begin{array}{cc}x&y&5&20&8&8\end{array}\right]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/business/college/si63k8hlco9we6wqu6omjf94ary1srkl6z.png)
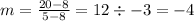
Then we solve for h
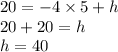
Demand would be y = -4x +40
We repeat the process with supply
![\left[\begin{array}{cc}x&y&1&26&3&38\end{array}\right]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/business/college/vvkzpupz3lcwyhlmt92m537izcv90temgn.png)
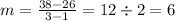
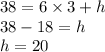
Supply is y = 6x + 20
Now we can solve for equilibrium price
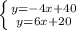
-4x + 40 = 6x + 20
20 = 10x
x = 20/ 10 = 2 price
And quantity
6 x 2 + 20 = 32
-4x2 + 40 = 32