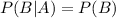Answer:
- The two events are independent.
Explanation:
By the conditional property we have:
If A and B are two events then A and B are independent if:
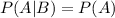
or
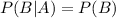
( since,
if two events A and B are independent then,
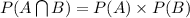
Now we know that:
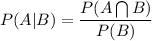
Hence,
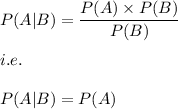 )
)
Based on the diagram that is given to us we observe that:
Region A covers two parts of the total area.
Hence, Area of Region A= 72/2=36
Hence, we have:
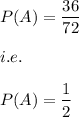
Also,
Region B covers two parts of the total area.
Hence, Area of Region B= 72/2=36
Hence, we have:
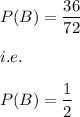
and A∩B covers one part of the total area.
i.e.
Area of A∩B=74/4=18
Hence, we have:
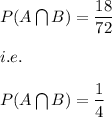
Hence, we have:
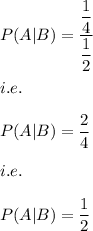
Hence, we have:
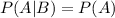
Similarly we will have: