Answer:
Step-by-step explanation:
For any system in equilibrium, the molar concentration of all the species on the reactant side are related to those on the product side by a constant known as the equilibrium constant
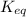 .
.
For a given reaction:
aA + bB ⇄ cC
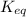 =
=
![([C]^(c) )/([A]^(a) [B]^(b) )](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/middle-school/qtgzqgiohn48szouewdavgu62in9bfk22e.png)
The reaction equation is given as:
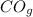 + 2H₂
+ 2H₂
 ⇆CH₃OH
⇆CH₃OH

Note: All the species are in gaseous phase.
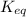 =
=
![([CH_(3)OH ])/([CO] [H_(2)] )](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/middle-school/m1i850pl1mnh5lrawrtxz65t039hp7duk8.png)