Answer:
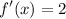
General Formulas and Concepts:
Calculus
Limits
Limit Rule [Constant]:
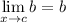
Differentiation
- Derivatives
- Derivative Notation
- Definition of a Derivative:
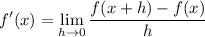
Explanation:
Step 1: Define
Identify
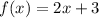
Step 2: Differentiate
- Substitute in function [Definition of a Derivative]:
![\displaystyle f'(x) = \lim_(h \to 0) ([2(x + h) + 3] - (2x + 3))/(h)](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/mathematics/middle-school/kxg6z5l8nmv586m341fl7f36kd0v032f2x.png)
- Expand:
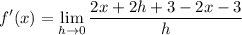
- Combine like terms:
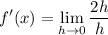
- Simplify:
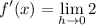
- Evaluate limit [Limit Rule - Constant]:
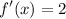
Topic: AP Calculus AB/BC (Calculus I/I + II)
Unit: Differentiation