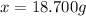Answer:
18.700 g
Step-by-step explanation:
As the urea is a nonvolatile and nonelectrolyte solute, it will reduce the vapor pressure of the solution according to:
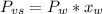
Where
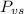 is the vapor pressure of the solution,
is the vapor pressure of the solution,
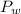 is the vapor pressure of the pure water, and
is the vapor pressure of the pure water, and
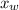 is the molar fraction of water. This equation applies just for that kind of solutes and at low pressures (23.76 mmHg is a low pressure).
is the molar fraction of water. This equation applies just for that kind of solutes and at low pressures (23.76 mmHg is a low pressure).
From the equation above lets calculate the water molar fraction:
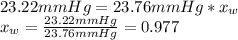
So, the molar fraction of the urea should be:
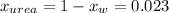
Then, calculate the average molecular weight:
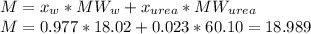
The molar fraction of urea is:
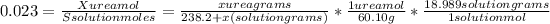
Solving for x,