Answer:
Part 1) The greater unit rate of the two functions is the linear function of the table
Part 2) The greater y intercept of the two functions is the linear equation of the graph
Explanation:
we know that
The rate of a linear function is equal to the slope
step 1
Find the slope of the linear equation in the table
we have
(0,5) and (5,15)
The slope is equal to
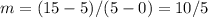
To find the unit rate divide by 5 both numerator and denominator
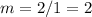
step 2
Find the slope of the linear equation of the graph
we have
(-4,0) and (0,6)
The slope is equal to
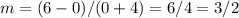
To find the unit rate divide by 2 both numerator and denominator
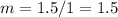
Compare the unit rate of the two linear equations
2 > 1.5
therefore
The greater unit rate of the two functions is the linear function of the table
step 3
Find the y-intercepts of the linear equations
Remember that the y-intercept is the value of y when the value of x is equal to zero
Linear equation of the table
Observing the table
For x=0, y=5
therefore
The y-intercept of the linear equation of the table is the point (0,5)
Linear equation of the graph
Observing the graph
For x=0, y=6
therefore
The y-intercept of the linear equation of the table is the point (0,6)
Compare the y-intercept both functions
6 > 5
therefore
The greater y intercept of the two functions is the linear equation of the graph