Answer : The
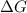 for this reaction is, -88780 J/mole.
for this reaction is, -88780 J/mole.
Solution :
The balanced cell reaction will be,
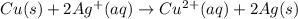
Here, magnesium (Cu) undergoes oxidation by loss of electrons, thus act as anode. silver (Ag) undergoes reduction by gain of electrons and thus act as cathode.
The half oxidation-reduction reaction will be :
Oxidation :
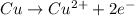
Reduction :
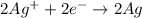
Now we have to calculate the Gibbs free energy.
Formula used :
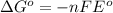
where,
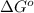 = Gibbs free energy = ?
= Gibbs free energy = ?
n = number of electrons to balance the reaction = 2
F = Faraday constant = 96500 C/mole
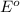 = standard e.m.f of cell = 0.46 V
= standard e.m.f of cell = 0.46 V
Now put all the given values in this formula, we get the Gibbs free energy.
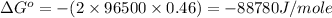
Therefore, the
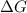 for this reaction is, -88780 J/mole.
for this reaction is, -88780 J/mole.