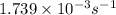Answer : The initial rate of the reaction is,
Explanation :
First we have to calculate the rate constant of the reaction.
Expression for rate law for first order kinetics is given by :
![k=(2.303)/(t)\log([A_o])/([A])](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/67w3lufh8bppkbbcp1xaut7f9029vt6k0l.png)
where,
k = rate constant = ?
t = time taken for the process = 44 s
![[A_o]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/high-school/38eb24kf04xqy5t88y9g0vzh3m04r4nqgg.png) = initial amount or concentration of the reactant = 0.1108 M
= initial amount or concentration of the reactant = 0.1108 M
![[A]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/ey5pxctwpmy356s81f6qc2pjl6oveugako.png) = amount or concentration left time 44 s = 0.0554 M
= amount or concentration left time 44 s = 0.0554 M
Now put all the given values in above equation, we get:
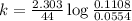
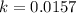
Now we have to calculate the initial rate of the reaction.
Initial rate = K [A]
At t = 0,
![[A]=[A_o]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/g6i1iikpgfeft2jm34yb6nokdq197xladt.png)
Initial rate = 0.0157 × 0.1108 =
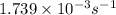
Therefore, the initial rate of the reaction is,