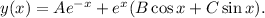Answer: The required general solution is
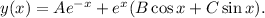
Step-by-step explanation: We are given to find the general solution of the following differential equation :

Let y = y(x) and
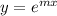 be an auxiliary solution of equation (i).
be an auxiliary solution of equation (i).
Then, we have
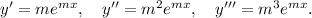
Substituting these values in equation (i), we have
![m^3e^(mx)-m^2e^(mx)+2e^(mx)=0\\\\\Rightarrow (m^3-m^2+2)e^(mx)=0\\\\\Rightarrow m^3-m^2+2=0~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~[\textup{since }e^(mx)\\eq0]\\\\\Rightarrow m^2(m+1)-2m(m+1)+2(m+1)=0\\\\\Rightarrow (m+1)(m^2-2m+2)=0\\\\\Rightarrow m+1=0~~~~~\Rightarrow m=-1](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/mathematics/college/fwnj6vinl3g16n6g0vtehjlclglequekyd.png)
and
![m^2-2m+2=0\\\\\Rightarrow (m^2-2m+1)+1=0\\\\\Rightarrow (m-1)^2=-1\\\\\Rightarrow m-1=\pm√(-1)\\\\\Rightarrow m=1\pm i~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~[\textup{where }i^2=-1]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/mathematics/college/ck1w1r6h49bv99ntfm13combrqttbikr6r.png)
So, we get
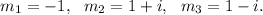
Therefore, the general solution of the given equation is given by
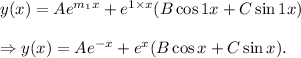
Thus, the required general solution is