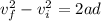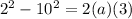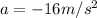Answer:
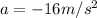
Step-by-step explanation:
As we know that the initial speed of the particle when it enters the nozzle is given as
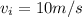
after travelling the distance d = 3 m it will have its final speed as
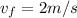
now we know that when acceleration is constant the equation of kinematics is applicable
so we will have