Answer:
Time taken, t = 3 s
Step-by-step explanation:
It is given that,
Initial velocity of the particle, u = 50 m/s
Final velocity, v = 20 m/s
Distance covered, s = 105 m
Firstly we will find the acceleration of the particle. It can be calculated using third equation of motion as :
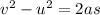
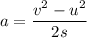
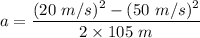
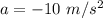
So, the particle is decelerating at the rate of 10 m/s². Let t is the time taken for the particle to slow down. Using first equation of motion as :
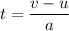
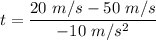
t = 3 s
So, the time taken for the particle to slow down is 3 s. Hence, this is the required solution.