Answer:
The correct answer option is A. the ratio increases as the pressure increases.
Step-by-step explanation:
We are to determine whether which of the given answer options explains how does a change in pressure affect the ration of PV to nRT.
We know that, for real gases:
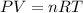
where,
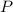 is the pressure of the gas ,
is the pressure of the gas ,
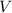 is the volume of gas ,
is the volume of gas ,
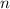 is the number of moles ,
is the number of moles ,
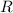 is the gas constant; and
is the gas constant; and
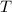 is the temperature of the gas.
is the temperature of the gas.
Gay-Lussac’s law states that for a constant volume, the pressure of that gas is directly proportional to the temperature on the Kelvin scale.
Therefore, the ratio increases as the pressure increases.