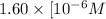Answer: B)
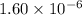 M, acidic
M, acidic
Step-by-step explanation:
pH or pOH is the measure of acidity or alkalinity of a solution.
pH is calculated by taking negative logarithm of hydrogen ion concentration and pOH is calculated by taking negative logarithm of hydroxide ion concentration.
Acids have pH ranging from 1 to 6.9, bases have pH ranging from 7.1 to 14 and neutral solutions have pH equal to 7.
![pH=-\log [H_3O^+]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/middle-school/xj6fwrpeduepfcp6k4cv1s827uf5c0pbp1.png)
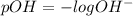
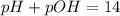
Given :
![[OH^-]=6.25* 10^(-9)M](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/bk2wgvnw15o0fgsjvhv7wzztddubzppbcb.png)
![pOH=-log[6.25* 10^(-9)M]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/m030yq8qv6i4hz60am6o95tx5lkv9r5vad.png)
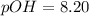
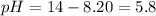
As pH is less than 7, the solution is acidic.
![5.8=-log[H_3O^+]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/psvzegwcowtzsjpjlrgb55rmody0iztex9.png)
![[H_3O^+]=1.60* [10^(-6)M](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/pp51ockwr1887mhzarr0icawrx9vvskzzq.png)
Thus solution is acidic and concentration of
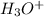 is
is