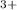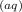What is the rate law for the uncatalyzed reaction?
In this type of reactions the rate law is dependent on the concentration of the reactants. In this case Ce and Tl ions. The answer will be rate=k[Ce
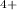 ]
]
 [Tl
[Tl
 ] because according to the rate law the reactants concentration should be powered at the number of moles, and from the equation we deduce that Ce
] because according to the rate law the reactants concentration should be powered at the number of moles, and from the equation we deduce that Ce
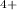 concentration will be powered to 2.
concentration will be powered to 2.
the other answers are wrong
If the uncatalyzed reaction occurs in a single elementary step, why is it a slow reaction?
“All reactions that occur in one step are slow” - it is not correct because there are one step reactions that are fast.
“The reaction requires the collision of three particles with the correct energy and orientation” - it is the correct answer because the particles should collide in exactly the same time with the required amount of energy for the reaction to take place. The probability of an effective three-particle collision is low so the reaction will be a slow one.
“The transition state is low in energy” - in this case the rate of the reaction should be fast because the energy for the reaction needed to take place is low.
The catalyzed reaction is first order in [Ce
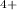 ] and first order in [Mn
] and first order in [Mn
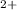 ]. Which of the steps in the catalyzed mechanism is rate determining?
]. Which of the steps in the catalyzed mechanism is rate determining?
rate =k[Ce
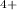 ] [Mn
] [Mn
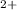 ] because the rate of the reaction may be done by increasing the amount of the catalyst (Mn
] because the rate of the reaction may be done by increasing the amount of the catalyst (Mn
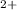 ).
).
The catalyzed reaction is first order in which of the steps in the catalyzed mechanism is rate determining?
Ce
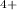
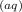 +Mn
+Mn
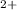
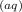 →Ce
→Ce
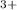
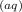 +Mn
+Mn