Answer: Nitric oxide is the limiting reagent. The number of moles of excess reagent left is 0.0039 moles. The amount of nitrogen dioxide produced will be 0.7912 g.
Step-by-step explanation:
To calculate the number of moles, we use the equation
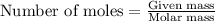 ....(1)
....(1)
Given mass of ozone = 0.827 g
Molar mass of ozone = 48 g/mol
Putting values in above equation, we get:
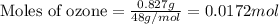
Given mass of nitric oxide = 0.635 g
Molar mass of nitric oxide = 30.01 g/mol
Putting values in above equation, we get:
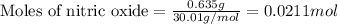
For the given chemical equation:
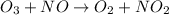
By Stoichiometry of the reaction:
1 mole of ozone reacts with 1 mole of nitric oxide.
So, 0.0172 moles of ozone will react with =
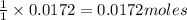 of nitric oxide
of nitric oxide
As, given amount of nitric oxide is more than the required amount. So, it is considered as an excess reagent.
Thus, ozone is considered as a limiting reagent because it limits the formation of product.
- Amount of excess reagent (nitric oxide) left = 0.0211 - 0.0172 = 0.0039 moles
By Stoichiometry of the reaction:
1 mole of ozone produces 1 mole of nitrogen dioxide.
So, 0.0172 moles of ozone will react with =
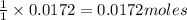 of nitrogen dioxide
of nitrogen dioxide
Now, calculating the mass of nitrogen dioxide from equation 1, we get:
Molar mass of nitrogen dioxide = 46 g/mol
Moles of nitrogen dioxide = 0.0172 moles
Putting values in equation 1, we get:
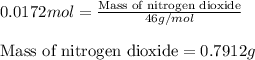
Hence, nitric oxide is the limiting reagent. The number of moles of excess reagent left is 0.0039 moles. The amount of nitrogen dioxide produced will be 0.7912 g.