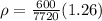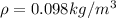Answer:
Step-by-step explanation:
As we know that for ideal gas we will have
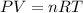
here we can convert it into the form of density
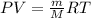
now we have
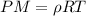
now if the temperature will remain constant then in that case
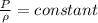
so we will have
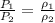
here we can plug in all values in it
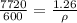
now we have