Answer: The enthalpy of the reaction for given amount of ammonia will be -3431.3 kJ.
Step-by-step explanation:
To calculate the number of moles, we use the equation:
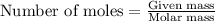
For ammonia:
Given mass of ammonia =
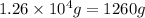
Molar mass of ammonia = 17 g/mol
Putting values in above equation, we get:
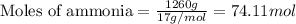
We are given:
Moles of ammonia = 74.11 moles
For the given chemical reaction:
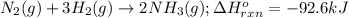
By Stoichiometry of the reaction:
If 2 moles of ammonia produces -92.6 kJ of energy.
Then, 74.11 moles of ammonia will produce =
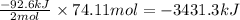 of energy.
of energy.
Thus, the enthalpy of the reaction for given amount of ammonia will be -3431.3 kJ.